Rolled Throughput Yield
Rolled Throughput Yield (RTY) is a process performance measure that provides insight into the cumulative effects of an entire process. RTY measures the yield across several process steps and provides the probability that a unit will traverse the process defect-free.
RTY allows us to expose the "hidden factory" by providing visibility into the yield of each process step. This helps us identify the poorest-performing process steps and provides clues on where to look for the most impactful process improvement opportunities.
In professional Six Sigma practice, Rolled Throughput Yield is taught, applied, and evaluated within structured DMAIC training and certification environments. It is used to assess cumulative process effectiveness across sequential steps, extending analysis beyond first-pass yield measures.
Calculating Rolled Throughput Yield (RTY):
RTY is found by multiplying the Yields of each process step. Let's take the 5-step process below and calculate its Rolled Throughput Yield using the abovementioned multiplication method.
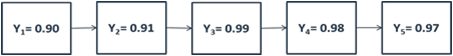
Abbreviations
- Defects = D
- Unit = U
- Defects per Unit = DPU
- Yield = Y
- e = 2.71828 (mathematical constant)
Yield Calculation
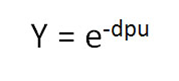
The Yield of a process step is the success rate of that step or the probability that the process step produces no defects. To calculate Yield, we need to know DPU, and then we can apply it to the Yield equation above.
For example, suppose a process step has a DPU of 0.109 or 10.9%, derived by dividing the number of defects (65) by units (598). Then, we can apply the Yield equation: Y = 2.718 ^ -0.109 = 0.8967 rounded, Y = 90%
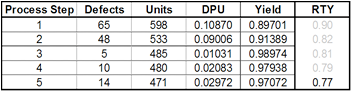
The table above uses the process yield data we used in the earlier RTY calculation. This table allows us to see the DPU and Yield of each step and the RTY for the whole process.
Estimating Yield
It is also possible to “estimate” Yield by taking the inverse of DPU or simply subtracting DPU from 1. Referring to the table above, let's run a quick yield estimation.
Yield Estimation = 1-DPU
- Yield Estimate for Process step 1 = 1 - 0.10870 = 0.89
- Yield Estimate for process step 2 = 1 - 0.09006 = 0.91
- Yield Estimate for process step 3 = 1 - 0.01031 = 0.99
- Yield Estimate for process step 4 = 1 – 0.02083 = 0.98
- Yield Estimate for process step 5 = 1 – 0.02972 = 0.97
RTY using the Yield Estimation Method = 0.89*0.91*0.99*0.98*0.97 = 0.76 or 76% PRETTY DARN CLOSE! And you don't even need the yield equation.
Rolled Throughput Yield in Six Sigma Practice
In formal Six Sigma practice, Rolled Throughput Yield is used to evaluate cumulative process performance across multiple sequential steps rather than evaluating steps in isolation. RTY highlights how small losses at each step compound across an end-to-end process.
Within structured DMAIC projects, RTY is commonly applied to:
- Reveal hidden process losses that are not visible through first-pass yield alone
- Compare end-to-end performance across alternative process designs
- Prioritize improvement efforts by identifying steps with the greatest impact on overall yield
- Support data-driven decisions during the Measure, Analyze, and Improve phases
Because RTY reflects compounded performance, it is most meaningful when interpreted alongside defect metrics, process capability analysis, and control planning rather than as a standalone measure.
About Lean Sigma Corporation
Lean Sigma Corporation is an independent Six Sigma certification authority responsible for the development, administration, and governance of professional Six Sigma credentials. The organization defines certification frameworks, examination standards, and credentialing systems used to evaluate and recognize Six Sigma competence across professional training environments.
Organizations and instructors delivering Six Sigma training under recognized standards participate in the Authorized Training Partner (ATP) Program.

