Moods Median Test with Minitab
What is Mood’s Median Test?
Mood’s median test is a statistical test to compare the medians of two or more populations.
- Null Hypothesis (H0): η1 = … = ηk
- Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): At least one of the medians is different from the others
The symbol k is the number of groups of our interest and is equal to or greater than two. Mood’s median is an alternative to Kruskal–Wallis. For the data with outliers, Mood’s median test is more robust than the Kruskal–Wallis test. It is the extension of one sample sign test. In a one-sample sign test, the null hypothesis is that the probability of a random value from the population being above the specified value is equal to the probability of a random value being below the specified value.
Mood’s Median Test Assumptions
- The sample data drawn from the populations of interest are unbiased and representative.
- The data of k populations are continuous or ordinal when the spacing between adjacent values is not constant.
- The k populations are independent to each other.
- The distributions of k populations have the same shape.
- Mood’s median test is robust for non-normally distributed populations.
- Mood’s median test is robust for data with outliers.
How Mood’s Median Test Works
Step 1: Group the k samples from k populations (sample i is from population i) into one single data set and get the median of this combined data set.
Step 2: Separate the data in each sample into two groups. One consists of all the observations with values higher than the grand median and the other consists of all the observations with values lower than the grand median.
Step 3: Run a Pearson’s chi-square test to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis.
- Null Hypothesis (H0): η1 = … = ηk
- Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): At least one of the medians is different from the others.
- If
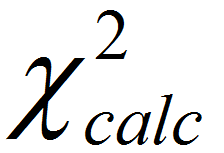 is greater than
is greater than 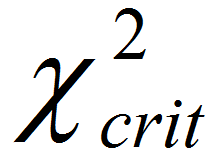 , we reject the null hypothesis and claim that at least one median is different from the others.
, we reject the null hypothesis and claim that at least one median is different from the others. - If
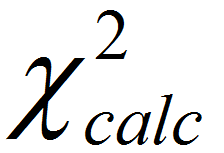 is smaller than
is smaller than 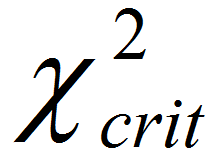 , we fail to reject the null hypothesis and claim that the medians of k populations are not statistically different.
, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and claim that the medians of k populations are not statistically different.
Use Minitab to Run a Mood’s Median Test
Case study: We are interested in comparing customer satisfaction among three types of customers using a nonparametric (i.e. distribution-free) hypothesis test: Mood’s median test.
Data File: “Median Test” tab in “Sample Data.xlsx”
- Null Hypothesis (H0): η1 = … = ηk
- Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): At least one of the medians is different from the others
Steps to run a Mood’s median test in Minitab
- Click Stat → Nonparametrics → Mood’s Median
- A new window named “Mood’s MedianTest” pops up.
- Select “Overall Satisfaction” as the “Response.”
- Select “Customer Type” as the “Factor.”

- Click “OK.”
- The Mood’s median test results appear in the session window.

Model summary: The p-value of the test is lower than alpha level (0.05), and we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that at least the overall satisfaction median of one customer type is statistically different from the others.
Join Our Community
Instant access to hundreds of "How to" articles, Tools, Templates, Roadmaps, Data-Files.. Everything Lean Six Sigma! Come on in! Welcome to our community of Lean Six Sigma certified professionals.

